Table of Contents
Introduction
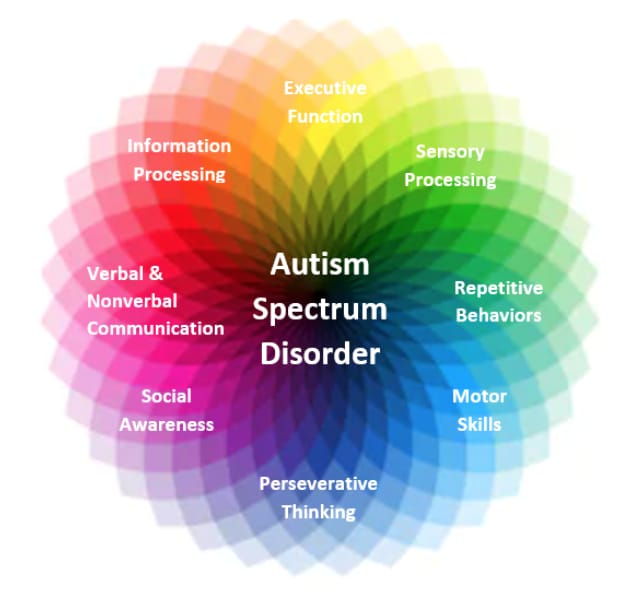
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition that impacts individuals in diverse ways, affecting their social interaction, communication, and behavior. Despite increased awareness in recent years, misconceptions and stigmas surrounding autism persist, often overshadowing the realities of those living with the condition. Understanding autism is crucial to providing appropriate support and fostering inclusivity within our communities.
The spectrum nature of autism means that no two individuals experience it in exactly the same way. Some may excel in certain areas while facing challenges in others, highlighting the importance of recognizing and embracing neurodiversity. However, myths and stereotypes about autism abound, perpetuating harmful misconceptions and hindering acceptance and understanding.
In this article, we will delve into the diverse world of autism, shedding light on the truths behind common misconceptions and exploring supportive strategies for individuals with ASD and their families. By debunking myths, providing insights into the realities of autism, and offering practical guidance, we aim to promote greater awareness, acceptance, and inclusivity for individuals on the autism spectrum.
Let us embark on a journey to uncover the complexities of autism and discover how we can create a more supportive and inclusive society for all
Demystifying Autism
Demystifying autism involves unraveling these misconceptions and shedding light on the realities of life on the autism spectrum. One common myth is that individuals with autism lack empathy or emotion. In truth, people with autism may experience and express emotions differently, but they are fully capable of forming deep and meaningful connections with others.
Another myth is that autism can be “cured” through interventions or treatments. While early intervention and support can improve outcomes and quality of life, autism is a lifelong condition, and there is no cure.
Understanding the diversity of the autism spectrum is essential to demystifying autism. The term “spectrum” reflects the wide range of abilities, challenges, and characteristics that individuals with autism may exhibit. Some individuals may have exceptional talents or skills in specific areas, while others may struggle with everyday tasks or social interactions. Recognizing and embracing this diversity is crucial to fostering acceptance and inclusion.https://youtu.be/hl0R7tDWLrc?si=FyNohs87zUkE-OX9
Demystifying autism also involves challenging stereotypes and promoting accurate portrayals of autism in the media and popular culture. Too often, individuals with autism are depicted as one-dimensional characters or portrayed solely through the lens of their diagnosis. By showcasing the full range of experiences and perspectives of individuals on the autism spectrum, we can dispel myths and promote understanding.

Ultimately, demystifying autism is about recognizing the humanity and worth of individuals with ASD. It’s about moving beyond labels and stereotypes to see the person behind the diagnosis, with their unique strengths, talents, and challenges. By fostering empathy, acceptance, and inclusivity, we can create a more supportive and understanding society for all individuals, regardless of neurodiversity.
Debunking Common Myths Surrounding Autism
Despite increased awareness and understanding of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in recent years, myths and misconceptions about the condition persist, perpetuating stigma and hindering acceptance. Debunking these myths is crucial to promoting accurate understanding and fostering inclusivity for individuals on the autism spectrum.
One common myth surrounding autism is that it is caused by bad parenting or childhood vaccines. This misconception has been thoroughly debunked by scientific research, which has found that autism has a complex and multifactorial etiology, with genetic and environmental factors playing significant roles. Blaming parents or vaccines not only perpetuates unfounded fears but also undermines the experiences of individuals and families affected by autism.
Another prevalent myth is that individuals with autism lack empathy or emotion. In reality, people with autism may experience and express emotions differently, but they are fully capable of forming deep and meaningful connections with others. Research has shown that individuals with autism can exhibit empathy and compassion, albeit in unique ways. By debunking this myth, we can promote greater understanding and acceptance of the diverse ways in which individuals on the autism spectrum experience and express emotions.
A third myth is that autism can be “cured” through interventions or treatments. While early intervention and support can improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals with autism, there is no cure for the condition. Autism is a lifelong neurodevelopmental disorder that manifests differently in each individual. Rather than focusing on “fixing” autism, efforts should be directed toward providing support, accommodations, and opportunities for individuals to thrive.
By debunking these and other myths surrounding autism, we can create a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals on the autism spectrum and their families. By promoting accurate understanding and dispelling misconceptions, we can foster empathy, acceptance, and appreciation for the unique strengths and challenges of individuals with autism.
Early Intervention
Early intervention in the case of autism refers to a proactive approach aimed at identifying and addressing the unique needs and challenges of children who are diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) at an early age. Early intervention is crucial in autism because it allows for timely support and intervention during a critical period of brain development, when the brain is most adaptable to change.https://youtu.be/2kirhUwF_5s?si=guWRfotuLeBxGh7z
Early intervention for autism typically involves a comprehensive and individualized approach that addresses the core areas affected by the condition, including social communication, behavior, and sensory processing. Some key components of early intervention for autism may include:
- Early Screening and Diagnosis: Identifying signs of autism as early as possible is essential for early intervention. Pediatricians, developmental specialists, and other healthcare professionals can conduct developmental screenings and assessments to identify red flags for autism and provide a formal diagnosis.
- Evidence-Based Interventions: Early intervention programs for autism often include evidence-based interventions that have been shown to be effective in improving outcomes for children with ASD. These may include applied behavior analysis (ABA), speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training.
- Individualized Treatment Plans: Each child with autism is unique, and their intervention plan should be tailored to their specific strengths, needs, and preferences. Early intervention teams work closely with families to develop individualized treatment plans that address the child’s unique challenges and capitalize on their strengths.
- Family Involvement and Support: Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in their child’s development and progress. Early intervention programs emphasize family-centered care, providing parents with education, training, and support to help them understand autism and learn strategies for supporting their child’s development at home.
- Collaboration and Coordination: Early intervention services often involve collaboration among a team of professionals, including therapists, educators, and healthcare providers. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that the child’s needs are addressed comprehensively and that interventions are coordinated across different settings, such as home, school, and community.

By providing early and intensive support, early intervention can help children with autism develop essential skills, improve their communication and social interaction abilities, and achieve their full potential. Research has shown that early intervention can lead to significant improvements in developmental outcomes and long-term success for children with autism. Therefore, accessing early intervention services as soon as possible after a diagnosis of autism is critical for maximizing the child’s chances of reaching their full potential.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment for individuals with autism involves implementing strategies and accommodations that promote their comfort, well-being, and success in various settings, including home, school, work, and community. Here are some key approaches to creating a supportive environment for autism:
- Structured and Predictable Routine: Establishing a structured and predictable daily routine can help individuals with autism feel safe, secure, and in control of their environment. Consistent routines can reduce anxiety and provide a sense of stability, making it easier for individuals with autism to navigate their day-to-day activities.
- Visual Supports: Visual supports, such as visual schedules, visual timers, and visual cues, can help individuals with autism understand expectations, transitions, and upcoming activities. Visual supports provide concrete and tangible information, which can be especially helpful for individuals who have difficulty processing verbal instructions or understanding abstract concepts.
- Sensory Accommodations: Many individuals with autism have sensory sensitivities or sensory processing differences. Creating a sensory-friendly environment involves minimizing sensory distractions and providing accommodations to support sensory needs. This may include using noise-canceling headphones, providing sensory-friendly lighting, or offering sensory tools such as fidget toys or weighted blankets.
- Clear and Direct Communication: Communication can be challenging for individuals with autism, so it’s important to use clear, direct, and concrete language when communicating with them. Avoiding ambiguous language, sarcasm, or figurative speech can help prevent confusion and misunderstandings.
- Social Skills Support: Individuals with autism may have difficulty understanding social cues, navigating social interactions, and making friends. Providing social skills support, such as social stories, role-playing activities, and peer mentoring programs, can help individuals with autism develop social skills and build meaningful relationships.
- Flexibility and Understanding: Flexibility and understanding are key when creating a supportive environment for autism. Recognize that individuals with autism may have different needs, preferences, and ways of interacting with the world. Being flexible and accommodating their individual needs can help create a more inclusive and supportive environment.
- Education and Awareness: Education and awareness are essential for creating a supportive environment for autism. Providing information about autism, raising awareness about the challenges faced by individuals with autism, and promoting acceptance and understanding can help foster a more inclusive and supportive community for individuals with autism and their families.
By implementing these strategies and accommodations, we can create a more supportive environment that respects and values the unique strengths and challenges of individuals with autism, enabling them to thrive and participate fully in all aspects of life.
Empowering Individuals with Autism
Empowering individuals with autism involves providing them with the tools, resources, and support they need to maximize their potential, pursue their interests, and lead fulfilling lives. Here are some key ways to empower individuals with autism:
- Building Self-Advocacy Skills: Empowering individuals with autism starts with helping them develop self-advocacy skills. This includes teaching them to identify their strengths, needs, and preferences, and advocating for themselves in various settings, such as school, work, and the community. By empowering individuals with autism to speak up for themselves and express their needs, they can become active participants in decision-making and self-determination.
- Fostering Independence: Encouraging independence is essential for empowering individuals with autism. This may involve teaching them life skills such as self-care, time management, and money management, as well as providing opportunities for them to practice and apply these skills in real-life situations. By fostering independence, individuals with autism can gain confidence, autonomy, and a sense of self-worth.
- Providing Assistive Technology: Assistive technology can be a powerful tool for empowering individuals with autism. This may include communication devices, visual supports, educational apps, and other assistive devices that can help individuals with autism overcome challenges and access information, communication, and learning opportunities. By providing assistive technology, individuals with autism can enhance their communication, independence, and participation in various activities.
- Offering Vocational Training and Employment Support: Empowering individuals with autism to pursue meaningful employment involves providing vocational training, job skills development, and employment support services. This may include job coaching, job placement assistance, and accommodations in the workplace to support individuals with autism in their job roles. By offering vocational training and employment support, individuals with autism can gain valuable skills, contribute to their communities, and achieve greater financial independence.
- Encouraging Participation in Community Activities: Encouraging individuals with autism to participate in community activities and social events can help them develop social skills, build connections, and expand their horizons. This may involve supporting them in joining clubs, sports teams, volunteer opportunities, or community groups where they can pursue their interests and engage with others who share similar passions.
- Promoting Inclusion and Acceptance: Promoting inclusion and acceptance is essential for empowering individuals with autism. This involves fostering a culture of understanding, respect, and support within families, schools, workplaces, and communities. By promoting inclusion and acceptance, individuals with autism can feel valued, respected, and appreciated for who they are, enabling them to thrive and reach their full potential.
Overall, empowering individuals with autism involves recognizing their strengths, supporting their needs, and promoting opportunities for them to participate fully in all aspects of life. By providing the necessary tools, resources, and support, we can empower individuals with autism to achieve their goals, pursue their passions, and lead fulfilling lives.
Supporting Families and Caregivers
Supporting families and caregivers of individuals with autism is paramount in ensuring the well-being and success of both the individual with autism and their support network. Families and caregivers often play a central role in the lives of individuals with autism, providing love, care, and support throughout their journey.
Firstly, providing families and caregivers with accurate information and resources about autism is essential. Understanding the condition and its impact can help families better support their loved one with autism and navigate the challenges they may encounter.
Access to services and support networks is also crucial for families and caregivers. Early intervention programs, specialized therapies, educational services, and support groups can provide invaluable assistance and guidance. These resources connect families with professionals and other individuals who understand their experiences and can offer practical advice and emotional support.
Respite care is another important form of support for families and caregivers. Caring for a loved one with autism can be physically and emotionally demanding, and respite care offers caregivers a much-needed break to rest and recharge. This temporary relief allows caregivers to maintain their own well-being and continue providing quality care to their loved one with autism.
Training and skill-building opportunities empower families and caregivers to effectively support their loved one with autism. Learning behavior management techniques, communication strategies, and advocacy skills equips caregivers with the tools they need to navigate the complexities of caring for someone with autism and advocate for their needs and rights.
Emotional support and counseling services are also vital for families and caregivers. Caring for a loved one with autism can be emotionally challenging, and having access to professional support can help caregivers cope with stress, anxiety, and burnout.
Financial assistance and advocacy resources further support families and caregivers in their caregiving journey. The costs associated with caring for someone with autism can be significant, and financial assistance programs can help alleviate some of the financial burdens. Advocacy resources empower families to advocate for their loved one’s rights and access to necessary services and supports.
In conclusion, supporting families and caregivers of individuals with autism is essential for promoting the well-being and resilience of both the individual with autism and their support network. By providing information, access to services, respite care, training, emotional support, financial assistance, and advocacy resources, we can empower families and caregivers to navigate the challenges of caring for someone with autism effectively. Together, we can create a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals with autism and their families, where everyone can thrive and reach their full potential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals in diverse ways, impacting their social interaction, communication, and behavior. Despite the challenges associated with autism, individuals on the spectrum possess unique strengths, talents, and perspectives that enrich our communities.
Understanding and acceptance are essential in creating a supportive environment for individuals with autism. By debunking myths, promoting awareness, and fostering inclusivity, we can create a society where individuals with autism are valued, respected, and given the opportunity to thrive.
Early intervention plays a crucial role in maximizing outcomes for individuals with autism. By providing timely support and interventions, we can help individuals with autism develop essential skills, improve their quality of life, and reach their full potential.
Supporting families and caregivers of individuals with autism is equally important. By providing information, access to services, respite care, training, emotional support, financial assistance, and advocacy resources, we empower families and caregivers to provide the best possible care and support for their loved ones with autism.
Ultimately, by working together to promote understanding, acceptance, and support, we can create a more inclusive and compassionate society where individuals with autism are embraced for who they are, and where they can thrive and contribute their unique talents and perspectives to the world.
For more such informative article you can visit the link https://telecastindia.in/?p=4484

Discover more from Telecast India
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

